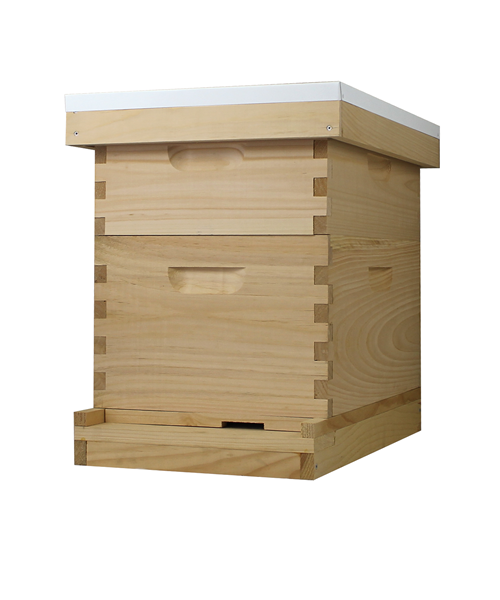
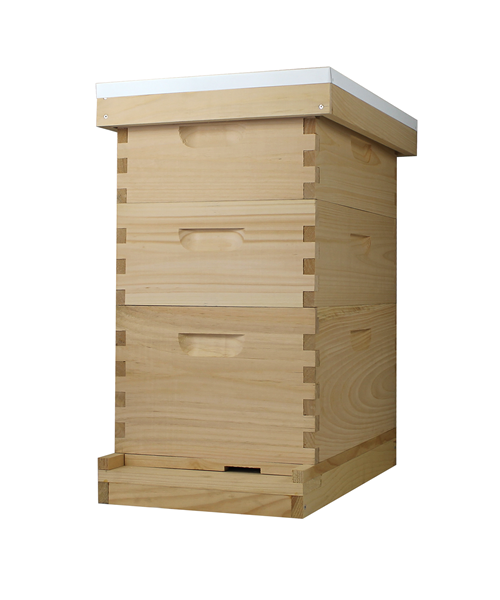
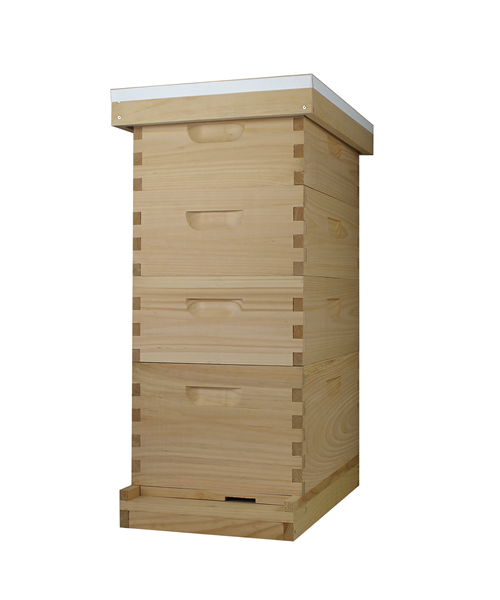
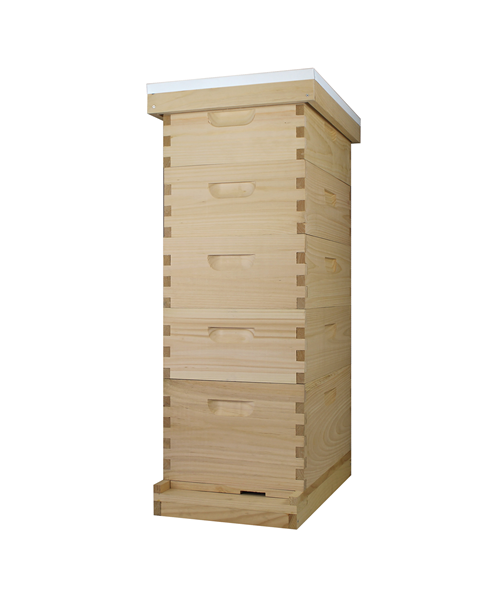
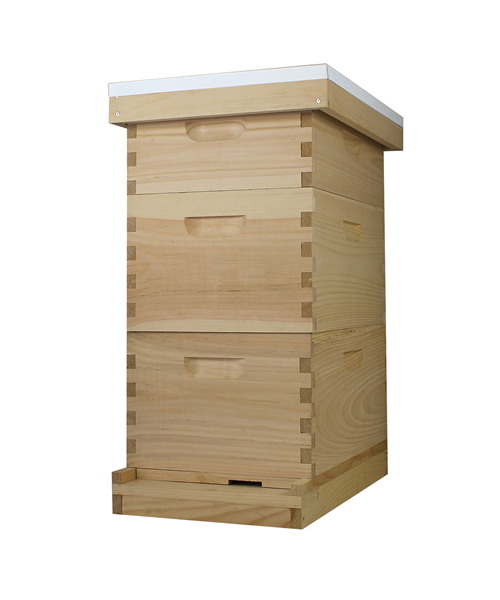
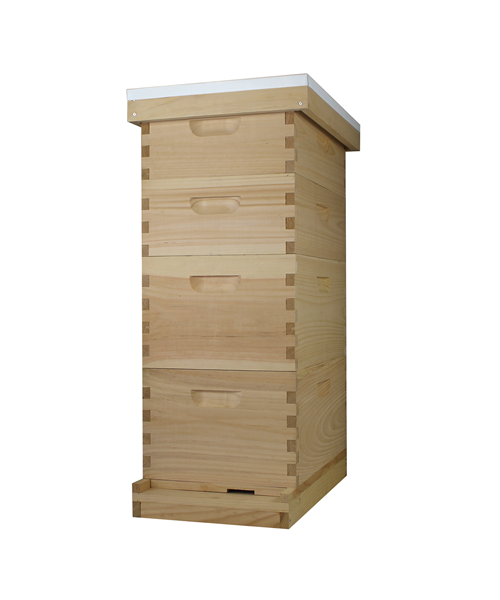
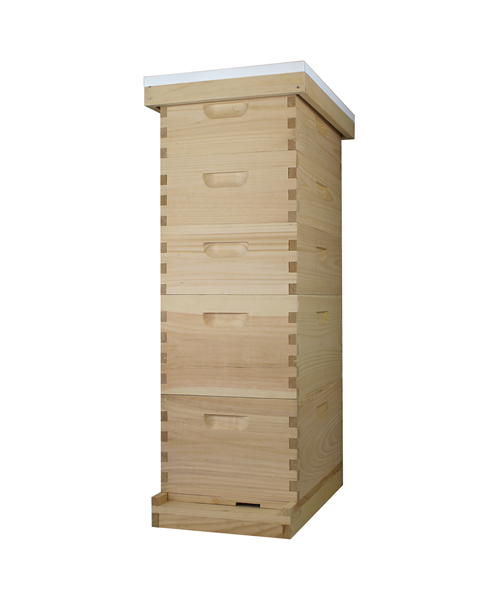
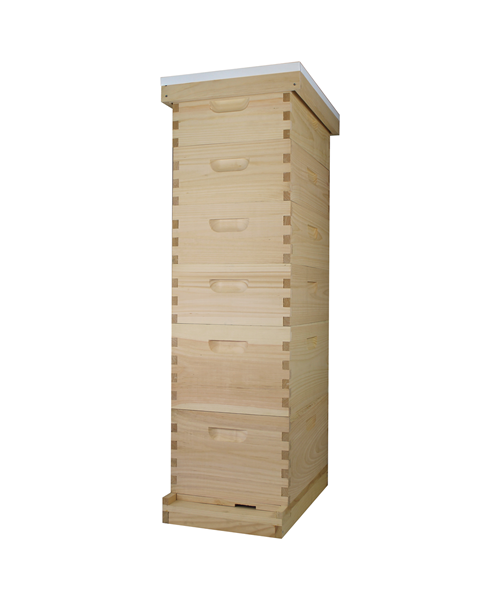
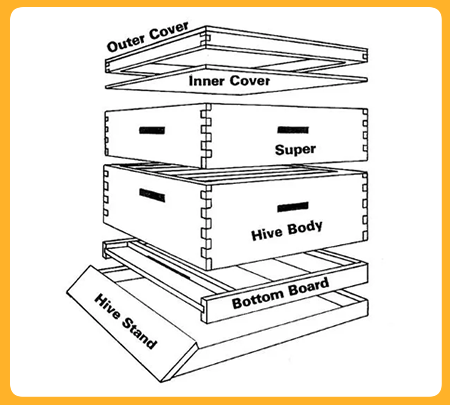
What is beehive ?
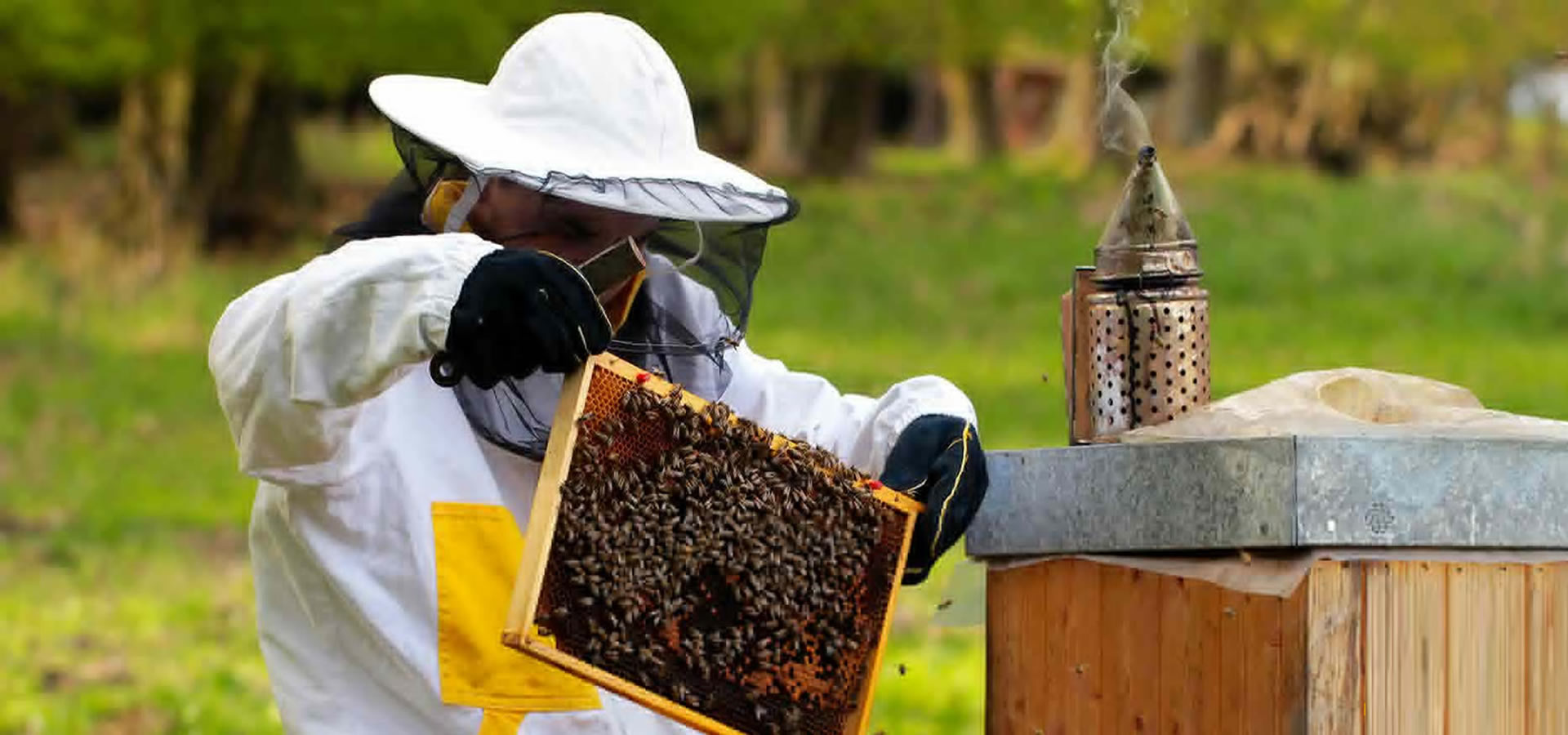
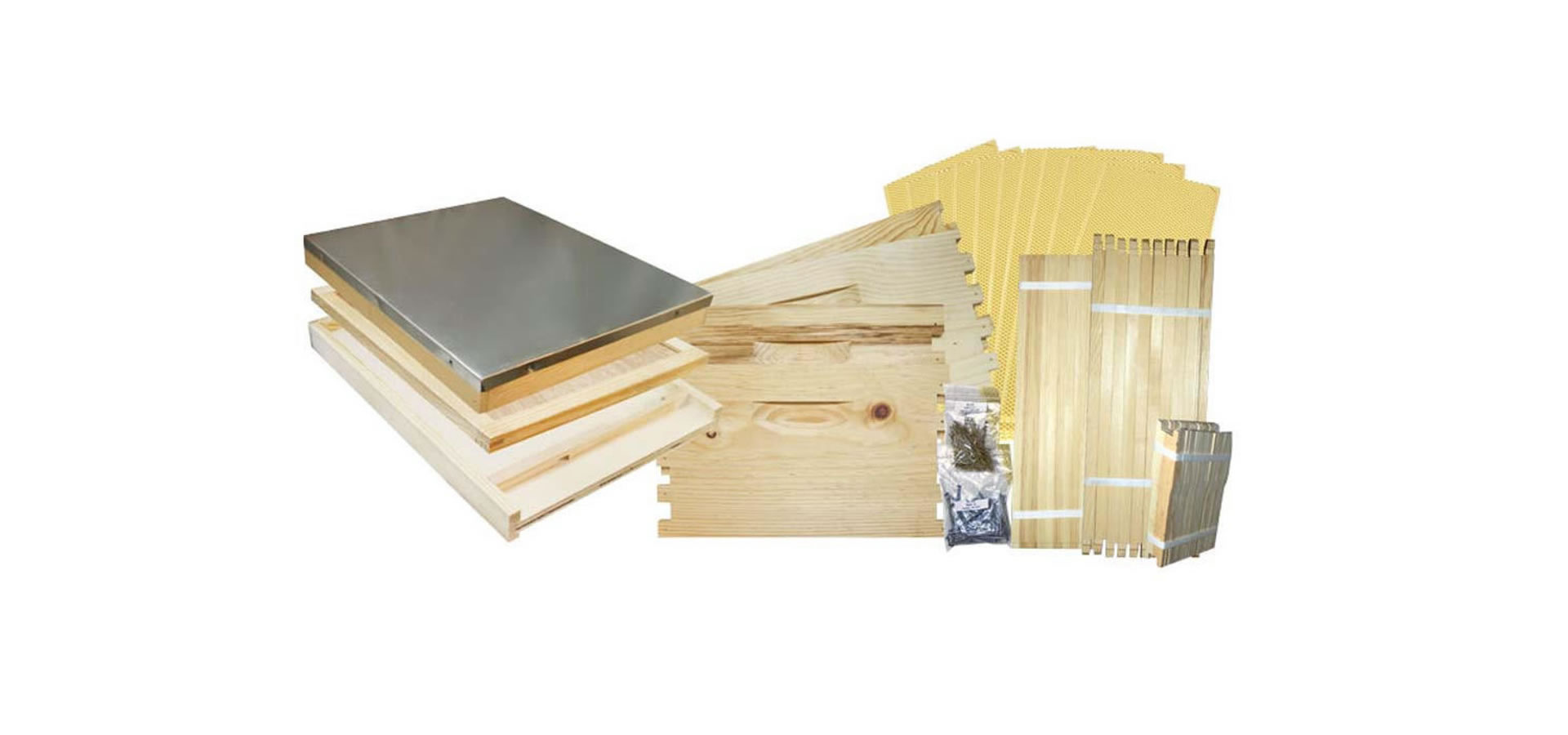
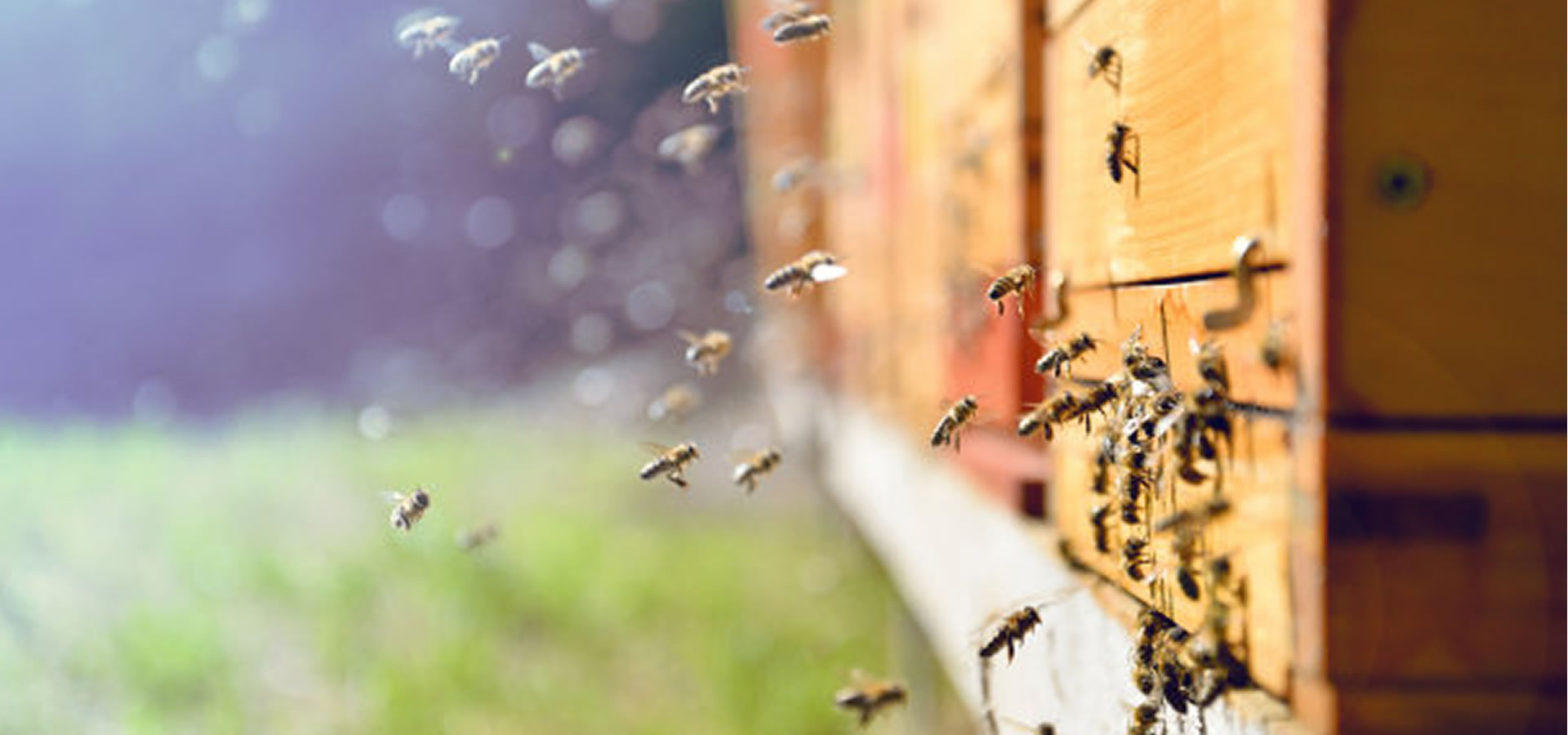
The beehive is a marvel of natural engineering, a bustling sanctuary where thousands of worker bees tirelessly toil together in perfect harmony. Within its wooden walls, they construct intricate hexagonal cells from beeswax, meticulously crafting the honeycomb that serves as their home and food storage. Each hive is a vibrant community, governed by the queen bee and her devoted subjects, all united in their singular mission to sustain the colony and perpetuate life.
In the gentle hum of BEEKEEPINGhive ihabitants and the golden sweetness of its honey, we whispers timeless lessons of unity, perseverance, and the beauty of collective effort.
Read More